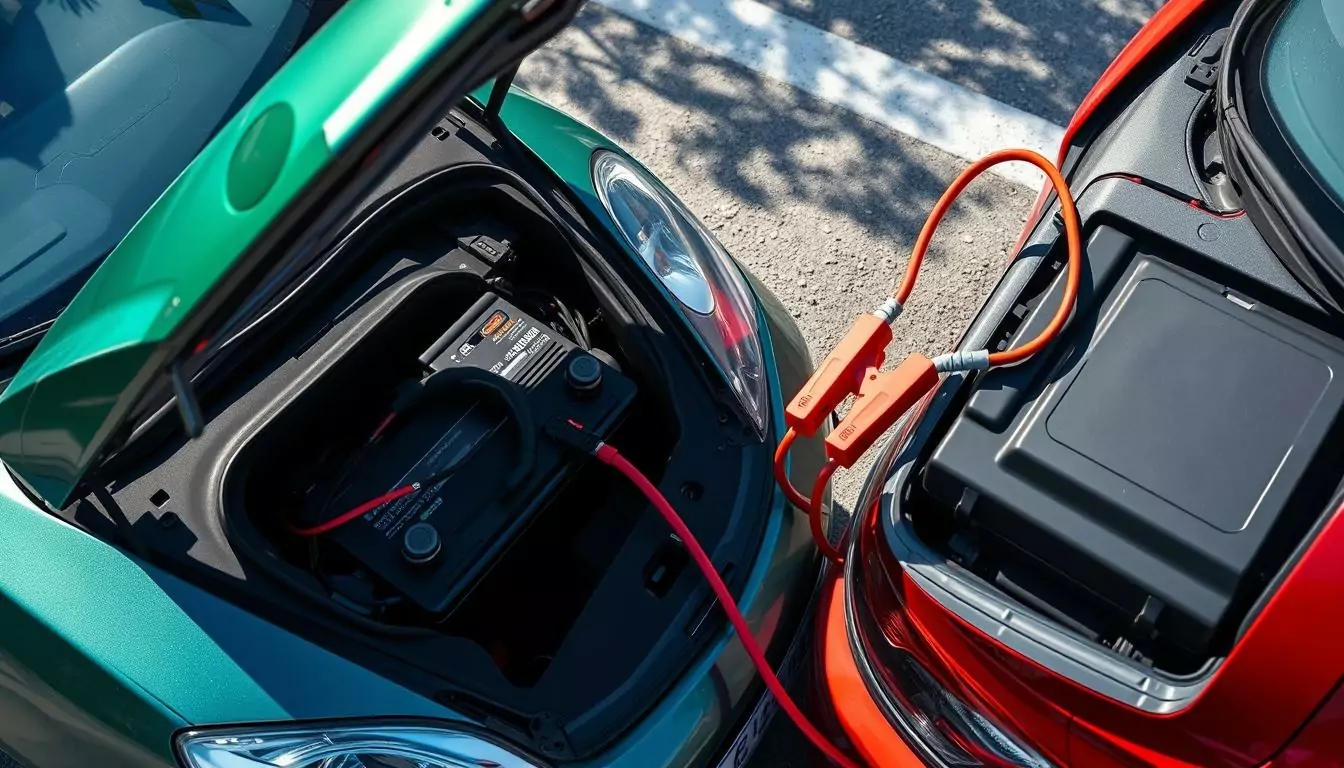
Ever been stuck with a dead car battery, staring blankly under the hood? Trust me, I’ve been there too. Jump starting a car isn’t just about slapping on some cables and crossing your fingers—it’s a handy skill that blends a bit of science, a dash of safety, and a whole lot of relief when your engine roars back to life. Whether it’s a frosty morning or you accidentally left the headlights on (oops!), this guide’s got you covered. Let’s dive into everything you need to know to jump start your car like a pro in 2025!
Why Jump Starting Is More Than Just Cables
Jump starting isn’t some mysterious car trick—it’s straight-up electrical magic. When you hook up a charged battery to a dead one, you’re creating a circuit that sparks a chemical reaction inside the battery. Pretty neat, right? That jolt is what gets your car humming again.
Today’s jump starters make it even easier. They’re lightweight, often powered by lithium-ion tech, and packed with safety goodies like overcurrent protection. So, even if you mix up the cables (we’ve all been there), you’re less likely to zap your car’s electronics.
- Completes a circuit between batteries—simple but brilliant.
- Kicks the dead battery’s chemistry back into gear.
- Lithium-ion jump starters: small, mighty, and easy to carry.
- Safety features to save you from newbie slip-ups.
Car Batteries 101: What’s Under the Hood?
Car batteries are the unsung MVPs of your ride. They kick the engine into action, keep your tunes playing, and power all those fancy gadgets. How? By turning chemical energy into electrical juice—think of it as a mini power station tucked under your hood.
Once you’re rolling, the alternator takes over, recharging the battery as you drive. Knowing this isn’t just car nerd trivia—it’s the foundation for nailing a safe jump start. You wouldn’t fix a sink without understanding water flow, so let’s get the basics down!
Types of Car Batteries
Most cars run on lead-acid batteries—they’re affordable and get the job done. But if you’ve got a snazzy new model, you might spot a lithium-ion battery. They’re lighter, last longer, and are showing up in more high-end rides these days.
Why Do Batteries Die?
Batteries usually last 3-5 years, but they’re not bulletproof. Freezing weather can zap their strength, leaving the lights on drains them quick, and good ol’ age eventually takes its toll. If your battery’s giving you grief too often, it might be time for a replacement.
The Magic Behind Electrical Circuits
Electrical circuits are the secret sauce of jump starting. Imagine a dead battery as a phone with no signal—useless until you plug it into something alive. Linking it to a charged battery forms a temporary circuit, letting power flow and waking up your car.
I once jumped my buddy’s truck in a rainy parking lot. Figuring out positive to positive, negative to ground felt like a game—nail the pattern, and you’re golden. It’s simple once you get the hang of it!
Quick Tips to Ace Jump Starting
- Shut off both cars before touching anything—safety first!
- Connect the positive terminals with the red clamp—piece of cake.
- Start the working car before trying the dead one.

Voltage: Your Battery’s Pulse
Voltage is what keeps your battery alive and kicking. Most car batteries run at 12 volts, hitting 12.6 when fully charged. With the engine off, anything between 12.4 and 12.7 volts is solid—dip below that, and you’ve got a problem brewing.
Low voltage creeps in from cold snaps or short drives that don’t give the alternator enough time to recharge. Noticed dim lights or a lazy startup? That’s your sign to grab the cables or test the battery.
| Battery Status | Voltage Range | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| Fully Charged | 12.6V – 12.7V | Relax—you’re good to go! |
| Okay | 12.4V – 12.5V | Watch it, just in case. |
| Low | 12.0V – 12.3V | Charge it up soon. |
| Dead Zone | Below 12.0V | Jump it or get a new one. |
Choosing the Best Jumper Cables
You wouldn’t sip a thick shake through a flimsy straw, so don’t cheap out on jumper cables either. The right set can make or break your jump start. Focus on gauge (thicker is better) and length—longer cables give you flexibility.
I’ve got a 20-foot, 4-gauge pair that’s saved my sedan more than once—worked like a charm every time. For bigger rigs, something like the Autogen 1-gauge packs the punch you need.
Safety Must-Haves for Cables
Go for spark-proof clamps and tough insulation—they’re your safety net. Some portable jump starters even have built-in cables with high-tech protections. Oh, and always flip through your car’s manual—some models have weird quirks you’ll want to know about.

How to Jump Start Your Car: Step-by-Step
Ready to be the roadside hero? Here’s how to jump start your car without sparking chaos. Follow these steps, and you’ll be back on the road in no time.
- Park the working car near the dead one—no bumper kissing required.
- Turn off both engines—let’s keep this safe.
- Clip the red cable to the dead battery’s positive terminal.
- Hook the other red end to the good battery’s positive terminal.
- Attach the black cable to the good battery’s negative terminal.
- Ground the other black end on unpainted metal in the dead car.
- Start the working car and let it run for a few minutes.
- Crank the dead car—fingers crossed!
I messed up the order once and got a mini spark show—yikes! Stick to this, and you’re set. Want a visual? Scroll up to the video!
Jump Starting FAQs: Your Questions, Answered
Can I Jump Start Any Car the Same Way?
Not exactly. Gas cars are straightforward, but hybrids and diesels need extra care. Diesels demand more power, and hybrids have tricky high-voltage setups. Peek at your manual to avoid surprises.
How Long Should I Charge Before Starting?
Let the working car run for 5-10 minutes to juice up the dead battery. After it starts, keep both engines on for 15-20 minutes to lock in the charge. Patience is your friend here!
What If My Car Still Won’t Start?
Check those connections—loose clamps can sabotage you. If it’s still dead, the battery might be kaput, or the alternator’s acting up. Time to call a pro if you’re stumped.
